One of the leading cloud data platforms, Snowflake, fell victim to a major cybersecurity breach in May 2024. The breach compromised data from major organizations, including Ticketmaster and Santander Bank, highlighting the weaknesses in cloud environments when it lacks efficient security measures.
How Did the Snowflake Breach Occur?
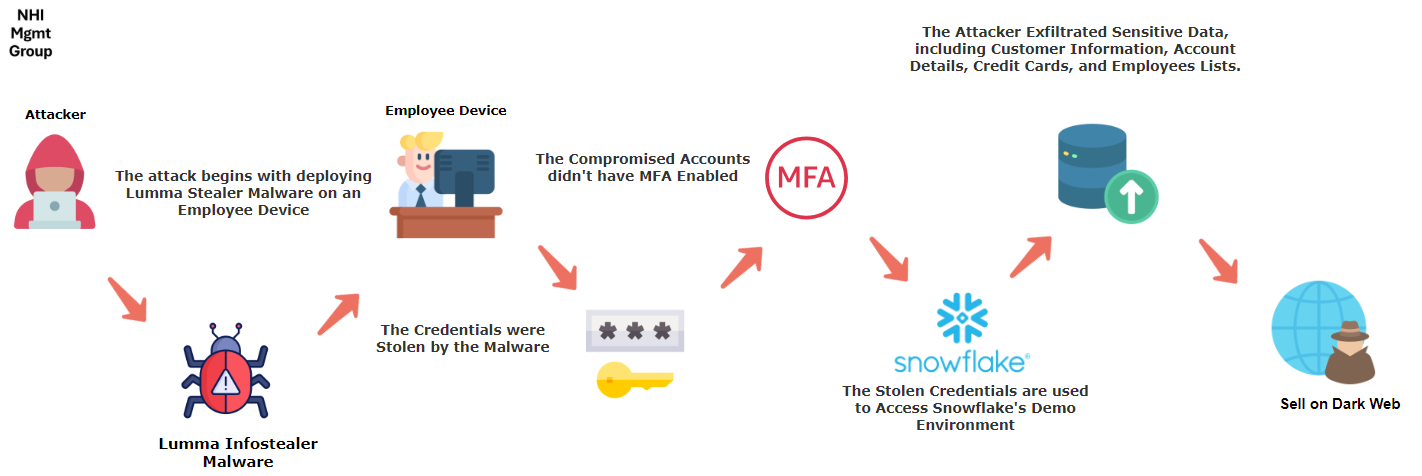
The incident began when Snowflake detected unauthorized access to its system. The attackers gained access to customer environments and demo accounts by using credentials that were stolen by an infostealer malware called Lumma Stealer. The attackers gained access to the data of several organizations hosted on Snowflake, using weaknesses such as:
- Lack of MFA: Some demo accounts were not secured with multi-factor authentication (MFA), which made it easy for the attackers to access the accounts.
Impacts of the Breach
The scope of the breach was extensive:
- Over 560 million users’ data from Ticketmaster, including payment details were leaked.
- Santander Bank customers’ information from multiple countries was also leaked.
- The attackers demanded $2 million ransom from Snowflake in exchange for stopping the sale of data.
How Did Snowflake Respond?
Snowflake hired cybersecurity experts to investigate and mitigate the breach. Their findings clarified that:
- The breach was not due to any vulnerabilities or misconfigurations in Snowflake’s infrastructure.
- Compromised credentials from infostealer malware were the primary attack vector.
- Demo environments were not protected by MFA, which granted initial access to the attackers.
Snowflake provided some recommendations for affected customers, emphasizing security practices such as MFA enforcement and regular credential rotation.
What’s Next?
Cloud platforms like Snowflake are critical to business operations, making them high value targets for cybercriminals. To mitigate risks, organizations need to:
- Ensure all accounts, including demo and low-priority environments, are protected by strong authentication mechanisms like MFA.
- Regularly rotate passwords and audit user access.
- Implement continuous monitoring and threat detection mechanisms to identify suspicious activities early.
- Frequent training for employees on recognizing phishing and malware threats.
Conclusion
This incident is a wake-up call for organizations relying on cloud platforms. By prioritizing security at all levels, businesses can properly protect their data and reputation against evolving threats.
