Govern the Mix: Static and Federated Non-Human Identities – Oasis Security
Static credentials constructs are increasingly misaligned with the needs of today’s cloud-first, rapidly evolving infrastructures, particularly as agentic AI (autonomous systems pursuing goals with limited supervision and tool-use) multiplies machine-to-machine exchanges and cross-service orchestration. But non-human identity isn’t binary. Most organizations will run a mix of static secrets and dynamic, federated identities for years. The real job is governance: pick the right method per use case, manage it well, and continually shrink standing privilege as your stack and maturity allow.
This article explores where static identity constructs struggle, where they still fit, and practical ways to manage both, along with a pragmatic path toward dynamic authentication. By addressing these issues, organizations can better safeguard their Non-Human Identities (NHIs) and reduce the risk of breaches in hybrid, multi-cloud, and AI environments.
Dynamic authentication is not just an advancement; it’s a direction of travel. Rotation, vaulting, and ownership still matter, but ephemeral, policy-driven access should be the default wherever it’s easy and supported.
Why Static Credentials Are Risky in Modern Environments
Static credentials, such as long-lived passwords, access keys, and API tokens, represent a persistent threat in modern IT environments. Their unchanging nature makes them a predictable and exploitable target for attackers (you find one, and you are golden for the foreseeable future!)
In cloud and hybrid infrastructures, static credentials often go unrotated or unmanaged, remaining valid long after their original purpose has expired, for instance, credentials created for an abandoned vendor evaluation or for a completed backup project that were never revoked. This creates vulnerabilities that attackers can exploit to gain unauthorized access. For example, unrotated credentials can be found embedded in source code or stored in unsecured locations, providing an easy entry point for malicious actors.
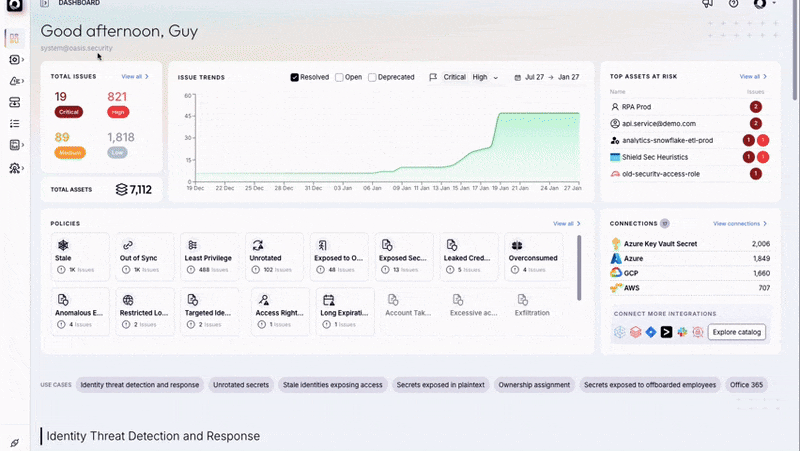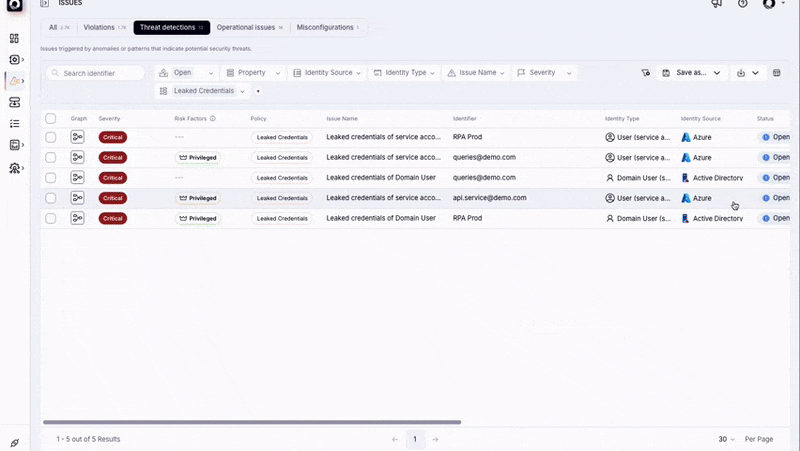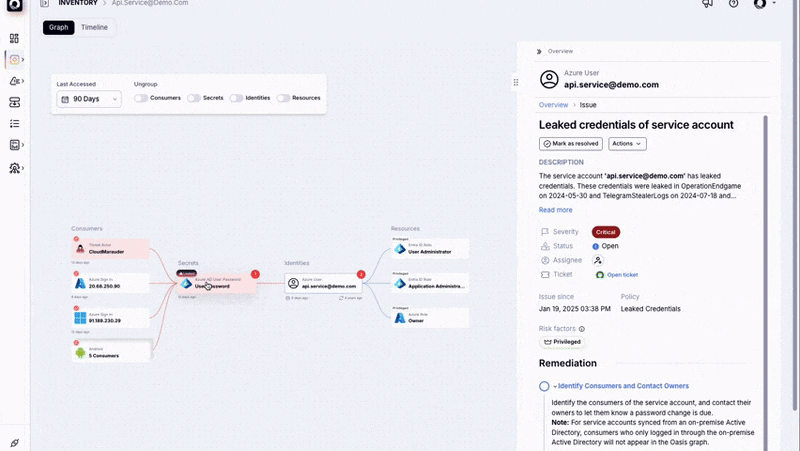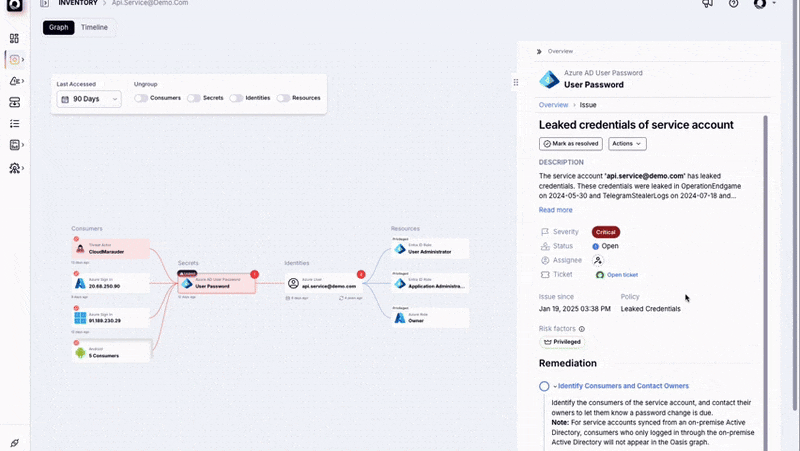
Data from security incidents highlights this risk. A 2024 survey by IBM revealed that static credentials contributed to over 60% of cloud-related breaches. Breaches involving static credentials cost organizations $4.81 million on average and require 292 days to contain, the longest remediation timeline of any attack vector, according to IBM’s 2024 Cost of a Data Breach. The McDonald’s breach, involving an AI hiring chatbot compromised by researchers utilizing the static credential “123456,” exemplifies the widespread issue of relying on static identity constructs. Such incidents underscore the inherent vulnerabilities when these unchanging identities are used in dynamic environments with rapidly evolving threats.
What Attackers Exploit When Credentials Never Change
Static credentials create opportunities for attackers to exploit weaknesses and gain unauthorized access. These risks are amplified in environments where credentials are not regularly monitored or updated.
Privilege Escalation
Attackers often use orphaned or unused credentials to elevate permissions within a system. Static service accounts, in particular, can retain excessive privileges long after their intended use. These credentials, when compromised, allow attackers to bypass security controls and gain broad access to sensitive resources.
Continuous identity posture review is essential to mitigate this risk. Regularly assessing permissions and revoking unnecessary access (least-privilege by default, and time-boxed access) significantly reduces the attack surface. Without this vigilance, static credentials can serve as hidden entry points for malicious activity.
API Key Harvesting
Hardcoded API keys and unrotated secrets are another common target for attackers. These credentials, often embedded in source code repositories or shared in collaboration channels, are easily accessible to anyone with access to the code. Public repositories, like GitHub, are frequently scanned by attackers seeking exposed keys. According to recent findings, 61% of organizations have secrets, like cloud credentials, exposed in public repositories. Once obtained, these credentials can be used to extract data, modify configurations, or disrupt services.
Automated tools that scan repositories for hardcoded secrets are critical in preventing such exposures. Combined with secure development practices, these tools help organizations identify and mitigate risks during the development process.
Lateral Movement
Static credentials enable lateral movement across systems, particularly in multi-cloud environments where identity sprawl is common. Once attackers gain access to one set of credentials, they can pivot to other systems by exploiting trust relationships and overprivileged accounts.
Real-time anomaly detection can help identify lateral movement. Monitoring tools that flag unusual activity, such as credential use from unexpected locations or during irregular hours, are crucial for detecting and responding to these threats before they escalate.
Practical Ways to Transition from Static to Dynamic credentials
Dynamic authentication provides a more secure alternative to static credentials by enabling flexible, time-bound, and context-aware access. Transitioning to dynamic methods requires (1) adopting strategies that prioritize security and automation, and (2) containing the legacy while you migrate. Lets focus on the strategies to move to dynamic credentials:
- Dynamic Service Identities (Ephemeral Tokens)
Ephemeral tokens are a secure replacement for static credentials because they are valid only for short periods. They are generated dynamically and automatically refreshed, drastically reducing the window of opportunity in which attackers can abuse compromised credentials.
Major clouds already mint short-lived tokens for workloads (AWS IAM roles, Azure Managed Identities, GCP Workload Identity Federation, etc.). A process hits the metadata endpoint, grabs a fresh JWT or cert, and uses it to reach only the resources its role allows.
- Policy-Based Access
Dynamic policy engines allow organizations to grant permissions based on contextual factors, such as user roles, device health, or the sensitivity of the requested resource. This ensures that access is only provided when necessary and under predefined conditions.
Integrating policy-based access with zero-trust frameworks enhances security by continuously verifying identity and access requirements. This model prevents overprovisioning and ensures that permissions are tailored to specific tasks or sessions.
- Just-in-Time Provisioning & Zero-standing privilege
Just-in-time provisioning eliminates the persistence of static credentials by issuing them only when required and revoking them shortly after use. This approach minimizes the risk associated with long-lived credentials while ensuring that access is both secure and efficient.
For DevOps and DevSecOps teams, just-in-time provisioning streamlines workflows by automating the issuance and removal of credentials. This reduces the administrative burden while maintaining strong security controls.
- Federation & Mesh
Adopt open trust frameworks:
- SPIFFE/SPIRE for per-process X.509 or JWT SVIDs, enabling mTLS inside and across clusters
- Workload-to-workload mTLS enforced by service meshes (Istio, Consul, etc.) for authenticated east-west traffic.
When Static Secrets Make Sense (and how to manage them well)
There are valid cases where static is the pragmatic fit: vendor APIs that only support keys, legacy/OT or air-gapped systems, certain cross-org workflows, or interim phases during migration.
Do this, every time:
- Vault & reference: Store centrally; never in code/images/chat. Inject via references.
- Assign ownership: Named owner and on-call. Track purpose, environment, blast radius, and renewal plan.
- Scope tightly: Resource-level scopes, least privilege, network/source restrictions, environment isolation.
- Automate rotation: Enforce max age; coordinate service-side change + client rollout; alert on failed/first use post-rotate.
- Instrument usage: Detect unusual geos/hours/volumes/clients; flag reuse across services.
- Right-size regularly: Remove unused scopes; disable stale keys; expire dormant service accounts.
- Practice revocation: Rehearse kill switches; measure MTTR to disable and recover.
Ensuring Continuous Threat Detection and Governance
Dynamic authentication and well-managed secrets both need continuous monitoring and governance to be effective. Real-time posture checks and anomaly detection play a critical role in identifying potential threats and ensuring compliance with security policies.
AI-driven analytics enhance detection by identifying deviations from normal behavior across systems. For example, AI can flag unusual credential usage patterns, such as access attempts from unexpected locations or devices, allowing security teams to respond proactively.
Governance frameworks must unify identity lifecycle management processes, enabling organizations to centralize functions like credential scanning, revocation, and periodic reviews. This ensures that all identities are effectively monitored and managed, reducing the risk of oversight or mismanagement.
Oasis Security for Future-Proof Identity Management
At Oasis Security, we recognize the limitations that static identity constructs impose on modern infrastructure. That’s why we built the Oasis NHI Security Cloud, to transform the way organizations manage and secure Non-Human Identities (NHIs) in dynamic, hybrid environments. Our platform enables companies to embrace the future by accelerating their journey toward federation and zero trust architectures.
Our platform combines advanced capabilities to address the vulnerabilities of static credentials and empower organizations to adopt dynamic authentication.
- Provision securely, by default
We integrate into your CI/CD, cloud, and identity stacks to provision NHIs with the most secure option from day one:
- Prefer managed identities where supported, selecting the method based on the identity’s purpose and the environment it runs in. SPIFFE/SPIRE is excellent for identities and mTLS within your own environment (clusters/VMs/services); for external SaaS, third-party, or cross-org access, use OIDC/SAML federation to the provider, or, if federation isn’t available, broker scoped API keys with short TTLs and rotation.
- Enforce least privilege at creation with guardrails and policy packs that align permissions to intended use.
- Federate & shorten lifetimes (dynamic auth)
We start with context & visibility: resolve ownership and map every consumer and usage path of each secret (services, pipelines, jobs, environments, third parties). Without this dependency map, migrating static creds to federation risks breakage.
We detect where static secrets are still used and, with that context, automatically recommend (if possible), and safely orchestrate, their migration to:
- Federated identities backed by your IdP/cloud provider.
- Ephemeral, auto-rotated credentials with minutes-to-hours TTLs.
- Policy-based issuance that adapts to context (workload, environment, identity posture).
Cutovers are dependency-aware (dual-issue/dual-validate), canaried, and include automatic rollback and post-cutover verification to ensure nothing breaks.
- Operate & defend what can’t (yet) be migrated
Where static credentials must persist, we minimize the blast radius:
- Automated remediation for overprivileged credentials to enforce least privilege.
- Continuous rotation & expiry enforcement for remaining secrets.
- Rapid anomaly detection with Oasis Scout to spot misuse in real time and trigger policy-driven containment.
- Lifecycle orchestration, end to end
Our policy-based lifecycle engine enforces consistent controls, from provisioning through decommissioning, across clouds, clusters, and runtimes.
By adopting Oasis NHI Security Cloud, organizations can eliminate static credentials, implement dynamic authentication, and achieve a security posture that is both adaptive and resilient.
- Post-secret posture: Design for federation and short-lived auth first; treat static credentials as legacy you’re actively shrinking.
- Actionable AI, not dashboards: Ownership resolved, migration paths generated, fixes automated.
- Continuous reduction of attack surface: Every day, fewer long-lived secrets, smaller privilege sets, shorter lifetimes.
Request a demo to see how Oasis Security can transform your identity management strategy: https://oasis.security/demo